If you’ve ever experienced a sudden loss of power while driving, you might be familiar with the dreaded P2106 code. It’s more than just a sequence of letters and numbers; it’s your vehicle’s way of signaling an issue within the throttle actuator control system.
Understanding what this code means is crucial for any car owner who wants to keep their ride in top shape. Let’s dive into the details about what causes the P2106 code, its symptoms, and how you can address it effectively!
Key Takeaway
The P2106 code indicates a problem with the throttle actuator control system, leading to limited engine power.
Drivers may experience reduced acceleration and unresponsive throttle response when this code triggers. This can make everyday driving feel like an uphill battle.
Understanding the symptoms is crucial for early detection. Ignoring this warning could lead to more complex issues down the line.
Common causes include faulty throttle bodies, wiring problems, or even sensor malfunctions. Regular maintenance can help prevent these problems from arising in the first place.
Addressing a P2106 code promptly not only improves vehicle performance but also enhances safety on the road. With timely intervention and proper diagnosis, you can keep your car running smoothly and efficiently without unexpected hiccups during your drive.
What does the P2106 code mean?
The P2106 code is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that indicates an issue with the throttle actuator control system. Essentially, it signals that your vehicle’s engine management system has detected a problem impacting the throttle position.
When this code is triggered, it often means that the engine’s power has been limited to protect against potential damage. The vehicle enters what’s known as “limp mode,” reducing its speed and performance.
This safety feature helps prevent further complications while allowing you to drive your car safely. Understanding this code can help prioritize repairs and maintain optimal engine function. Addressing issues linked to the P2106 promptly ensures better performance and longevity of your vehicle.
What are the common symptoms of a P2106 code?
When your vehicle triggers a P2106 code, several symptoms may emerge. You might first notice a sudden loss of power during acceleration. It can feel like the engine is struggling to respond.
The check engine light will likely illuminate on your dashboard as well. This warning serves as an alert that something isn’t right with the throttle actuator system.
Another common symptom includes erratic idling or stalling while driving. Your vehicle may hesitate before picking up speed, disrupting smooth transitions between gears.
Drivers often report unusual sounds coming from the throttle body area, such as buzzing or clicking noises. These sounds could signify underlying issues within the control system.
You might experience reduced fuel efficiency due to improper airflow regulation caused by a malfunctioning actuator. Keep an eye out for these signs if you suspect a P2106 code issue is at play.
What causes a P2106 code?
A P2106 code is triggered by issues within the throttle actuator control system. This system plays a critical role in regulating the air intake, impacting engine performance.
One common culprit is a malfunctioning throttle body. When this component fails to open or close properly, it disrupts airflow and triggers the error code.
Electrical problems can also cause trouble. Damaged wiring or corroded connectors may interfere with signals sent between the throttle position sensor and the engine control unit (ECU).
Additionally, software glitches in the ECU could lead to erroneous readings. These bugs might mistakenly signal that there’s an issue with throttle control when everything appears normal.
Vacuum leaks can create imbalances in air pressure, further complicating matters for your vehicle’s engine management system. Addressing these root causes quickly is vital for restoring optimal vehicle performance.
How is a P2106 code diagnosed?
Diagnosing a P2106 code begins with connecting an OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port. This tool retrieves the trouble codes stored in the engine control module (ECM).
The technician will check for any additional codes that might provide further insight into underlying issues. It’s essential to consider related symptoms, as they can point toward specific components.
Next, visual inspections of wiring and connectors around the throttle actuator are crucial. Damaged or corroded parts may contribute to this error code.
Functional tests of the throttle body and accelerator pedal position sensors follow. These assessments help determine if these components operate within specifications.
Mechanical tests ensure there are no vacuum leaks or other anomalies affecting performance. Accurate diagnosis requires a systematic approach, ensuring all potential causes are explored thoroughly before making repairs.
How do I fix a P2106 – Throttle Actuator Control System – Forced Limited Power ?
Fixing a P2106 code typically starts with inspecting the throttle position sensor and wiring. Look for frayed wires or loose connections that might disrupt communication between components.
Next, examine the throttle body itself. A dirty or malfunctioning throttle can cause issues. Cleaning it thoroughly may resolve some problems. If cleaning doesn’t help, consider replacing the throttle body.
Running a diagnostic test can also be beneficial to identify any additional trouble codes related to this issue. Address those as needed.
Additionally, check your vehicle’s battery health. A weak battery can lead to voltage issues affecting various systems, including the throttle actuator control system.
After making repairs or replacements, clear the trouble codes using an OBD-II scanner and take your car for a test drive to verify if the issue persists.
How much does it cost to fix a P2106 code?
The cost to fix a P2106 code can vary widely based on several factors. On average, you might expect to pay anywhere from $100 to $1,500 :
- Throttle body cleaning: $50-$125 USD
- APP sensor: $75-$300 USD
- TPS: $50-$200 USD
- Throttle actuator: $300-$650 USD
- ECM: $500-$1500 USD
Labor costs also add up based on where you live and your vehicle’s make and model. It typically range from $100 to $200 per hour, depending on the region and shop rates.
Are there any other codes that may be related to a P2106 code?
When troubleshooting the P2106 code, several related codes may also surface. These often point to underlying issues within the throttle control system or other interconnected components :
- P0121–P0124 (TPS faults)
- P0221-P0228 (APP sensor faults)
- P0506 (Idle RPM lower than expected)
- P0507 (Idle RPM higher than expected)
- P1516 (Throttle actuator control module)
- P2101–P2103, P2110-P2112 (Other throttle actuator faults)
Frequently Asked Questions About P2106 Code :
Can I still drive with a P2106 code?
Driving with a P2106 code is not advisable. This code indicates an issue with the throttle actuator control system, which can lead to reduced engine power. Your vehicle may enter a limp mode to protect itself from potential damage.
In this limited power state, acceleration becomes sluggish and unresponsive. You might find it difficult to merge into traffic or climb steep hills.
If you must drive, be cautious and aware of your surroundings. It’s essential to avoid high-speed situations until the problem is resolved.
Ignoring the P2106 code could result in further complications down the line. Prompt attention will help prevent costly repairs later on. Prioritize diagnosing and fixing the underlying issue for safer driving conditions moving forward.
What parts are involved with the P2106 code?
When dealing with the P2106 code, several key components play a critical role in its operation. :
- Accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor
- Throttle actuator motor
- Throttle position sensor (TPS)
- Throttle body assembly
- Associated wiring and connectors
- Engine control module (ECM)
Can a bad throttle body cause the P2106 code?
A bad throttle body can indeed trigger the P2106 code. The throttle body controls airflow into the engine, and any malfunction here affects performance.
When the throttle body is dirty or faulty, it may not open or close properly. This can lead to a loss of power when accelerating. In some cases, your vehicle might even enter limp mode to prevent further damage.
Signs of a failing throttle body include stalling and erratic idling behavior. If you notice these symptoms alongside the P2106 code, it’s worth investigating the throttle body’s condition.
Cleaning or replacing a damaged throttle body often resolves issues related to this code. Regular maintenance can help avoid such problems in the first place by keeping components clean and functional.
Can a weak battery cause code P2106?
A weak battery can indeed contribute to the P2106 code. When the battery doesn’t provide sufficient voltage, it may cause erratic behavior in various electronic systems.
The throttle actuator control system relies heavily on stable power supply. If the battery is failing or not charged properly, this can lead to unintended consequences like limited engine power.
Additionally, low voltage can trigger warning lights and codes that might confuse drivers about underlying issues. It’s essential to ensure your vehicle’s electrical components are functioning optimally before diving deeper into diagnostic trouble codes.
If you suspect a weak battery is at play, testing its voltage should be a priority. A healthy battery should typically read around 12.6 volts when fully charged.
Will disconnecting the battery clear the P2106 code?
Disconnecting the battery may temporarily clear the P2106 code, but it’s more like a quick fix than a solution. When you remove power from the vehicle’s electrical system, it resets the engine control module (ECM).
However, this doesn’t address the underlying issue causing the P2106 code. If there’s a persistent problem with your throttle actuator or any related components, chances are that once you reconnect everything and start driving again, the code will return.
It’s essential to diagnose why this error occurred in the first place. Ignoring it can lead to reduced engine performance and potential safety hazards while driving.
For lasting results, consider addressing any mechanical issues before simply resetting codes through disconnection methods. This proactive approach ensures your vehicle remains reliable on the road.
Can low oil cause the P2106 code?
Low oil levels can lead to various engine problems, but it’s important to note that they don’t directly trigger the P2106 code. However, inadequate lubrication may result in poor engine performance and potential overheating.
When an engine runs low on oil, friction increases among moving parts. This extra strain can affect the throttle actuator’s functionality indirectly. If the system struggles due to heat or wear from insufficient oil, it could send incorrect signals.
Reduced power output may also arise from these conditions. While a direct link between low oil and the P2106 code isn’t established, ensuring proper oil levels is vital for overall vehicle health. Neglecting this aspect can lead to complications down the line that might involve other diagnostic codes appearing alongside P2106.
Regular maintenance checks are essential not just for optimal performance but also for preventing unwanted issues related to your vehicle’s systems.
Can a vacuum leak cause the P2106 code?

A vacuum leak can indeed trigger the P2106 code. When there’s a gap in the intake system, it allows excess air to enter the engine. This disrupts the air-fuel mixture necessary for optimal performance.
The throttle actuator struggles to maintain control over this unregulated airflow. As a result, your vehicle may experience reduced power and stalling.
Identifying a vacuum leak often requires careful inspection of hoses and gaskets. Even small cracks can create significant issues.
Listening for hissing sounds during idle can help pinpoint leaks. Alternatively, using soapy water on suspected areas might reveal bubbles where air escapes.
Addressing vacuum leaks promptly is crucial for maintaining engine efficiency and preventing further complications with throttle control systems. Ignoring these signs could lead to more extensive repairs over time.
Can a clogged catalytic converter cause code P2106?
A clogged catalytic converter can indeed lead to the P2106 code. When it becomes blocked, exhaust gases cannot exit the engine efficiently. This restriction can cause various performance issues.
The throttle actuator control system relies on proper airflow for optimal operation. If the engine struggles due to back pressure from a clogged converter, it may trigger a forced limited power mode.
This situation prompts the vehicle’s computer to reduce engine output as a protective measure against potential damage. Drivers might notice reduced acceleration and overall sluggishness.
Addressing such blockages is crucial not just for resolving error codes but also for maintaining general vehicle health. Regular inspections of your exhaust system can help prevent these complications before they arise.
How long does it take to fix code P2106?
The time it takes to fix the P2106 code can vary significantly. It largely depends on the root cause of the issue and whether any additional problems are present.
If the problem is a simple one, like a loose connection or an air intake leak, repairs may only take an hour or two. Technicians might quickly address these minor issues during routine diagnostics.
However, if more complex components like the throttle body need replacement, you could be looking at several hours of labor. Parts availability can also affect repair time.
Is code P2106 the same as reduced engine power?
The P2106 code and reduced engine power are closely related but not identical. When the P2106 code triggers, it often indicates a throttle actuator control issue.
This situation typically leads to the car entering a fail-safe mode. In this mode, your vehicle limits its power output to protect the engine from potential damage.
Drivers may notice sluggish acceleration or an inability to reach higher speeds. This is part of the system’s strategy to prevent further complications while allowing you to drive at a reduced capacity.
While they occur simultaneously, it’s important to recognize that P2106 serves as an indicator of what’s going wrong rather than being synonymous with reduced engine power itself.
Can a bad mass air flow sensor cause the P2106 code?
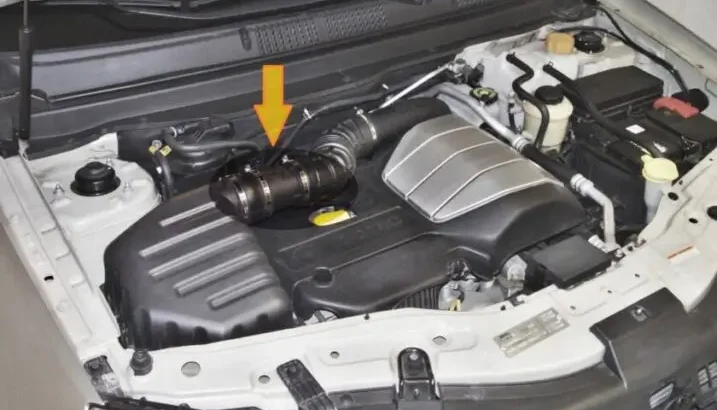

A bad mass air flow (MAF) sensor can indeed trigger the P2106 code. The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine, which is crucial for maintaining the correct fuel-to-air ratio.
When this component malfunctions, it sends incorrect readings to the Engine Control Unit (ECU). As a result, the ECU may struggle to adjust throttle response properly. This miscommunication can lead to reduced power and performance issues, prompting the system to activate limp mode.
Drivers often notice symptoms like stalling or erratic acceleration alongside other warning lights on their dashboard. Addressing MAF sensor problems promptly is essential; otherwise, they could compound into more significant issues with your vehicle’s throttle control system.
Can a bad O2 sensor cause code P2106?

A malfunctioning O2 sensor can indeed contribute to the P2106 code. The oxygen sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring exhaust gases and providing feedback to the engine control unit (ECU). If it fails, it may provide incorrect data.
When this happens, the ECU might adjust fuel delivery improperly. This miscalculation can lead to performance issues that trigger various codes, including P2106.
While a bad O2 sensor isn’t the direct cause of the throttle actuator control system error, its impact on engine performance creates conditions ripe for triggering such codes.
Addressing an O2 sensor issue promptly is essential. Ignoring it could exacerbate other problems within your vehicle’s systems, leading to further complications down the line. Regular diagnostics can help identify whether an O2 sensor issue is at play when dealing with P2106 and related symptoms.
What is the difference between code P2106 and P2135?
When comparing the P2106 code to the P2135 code, it’s important to understand their distinct meanings. The P2106 code refers specifically to a problem with the throttle actuator control system and indicates that power is limited due to an issue detected by the vehicle’s computer. On the other hand, the P2135 code relates directly to throttle position sensors. It signals a discrepancy between two sensors measuring throttle position, indicating they aren’t providing consistent readings.
While both codes can affect engine performance and lead drivers into a reduced power mode, they originate from different components of your vehicle’s electronic systems. Addressing these codes effectively requires knowledge of their specific symptoms and causes. Keeping this in mind helps ensure you properly diagnose issues without confusion between similar-sounding trouble codes like P2106 and P2135. Understanding these differences not only aids in repairs but also ensures better maintenance practices for your vehicle going forward.
